Production Scheduling Identification: Using Smart Meter Data to Infer Industrial Load Parameters
Published in IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2024
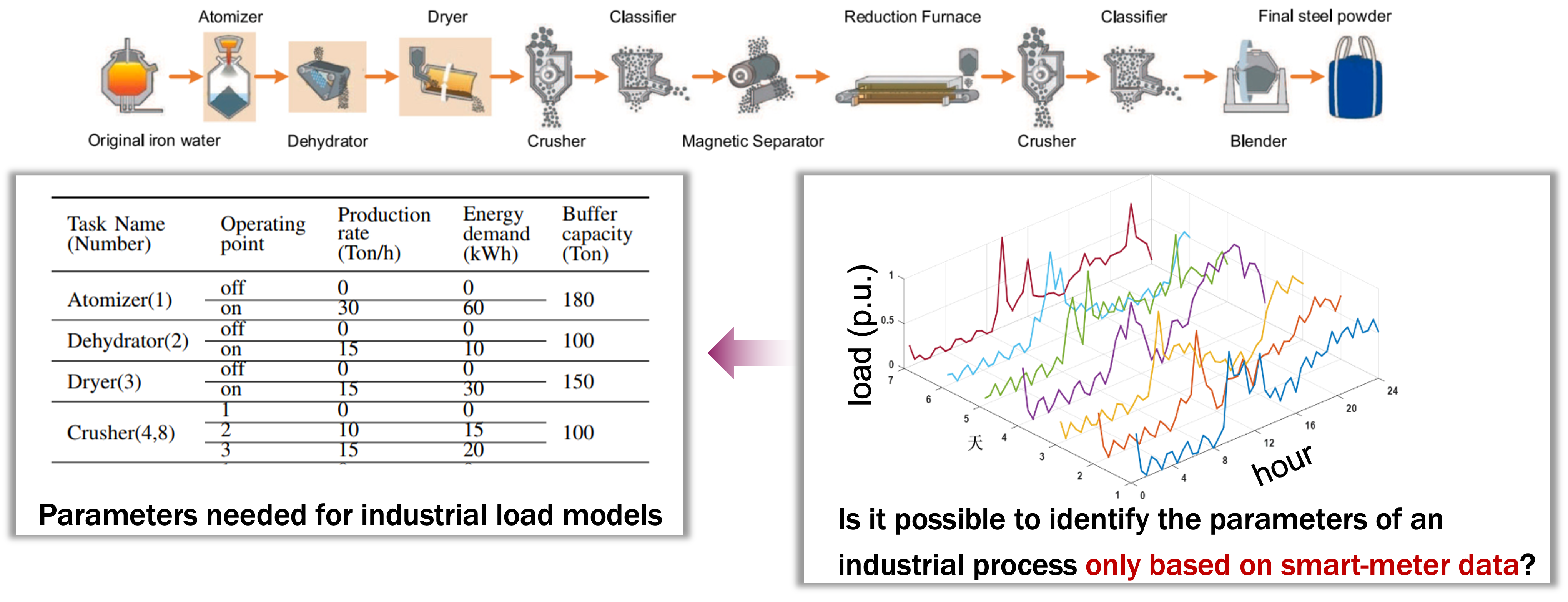
The Parameter Challenge
Even with accurate industrial load models, a significant challenge remains: the parameters needed for these models are often inaccessible to virtual power plants or power grid operators. These parameters—such as rated power, storage buffer sizes, and production equipment specifications—are typically considered commercially sensitive or private information. This creates a fundamental obstacle in implementing industrial load flexibility at scale.
Existing Approaches and Their Limitations
For decades, researchers have worked on Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM) techniques to extract information about loads without installing new measurement equipment. These methods attempt to disaggregate total power measurements to identify individual devices and their characteristics.
However, traditional NILM approaches face a critical limitation: they require high-resolution measurement data (often at millisecond intervals) to be effective. This requirement makes them impractical for large-scale industrial implementation, where:
- Typical measurement resolution is 1 hour
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (smart meters) might provide 15-minute resolution
- Even this improved resolution was considered insufficient for parameter identification
Our Breakthrough Approach
We developed a novel method that overcomes these limitations by combining two key insights:
- Economic behavior assumption: Industrial users will optimize their operations to minimize electricity costs in response to external electricity prices
- Production process knowledge: Leveraging domain knowledge about standard industrial production processes
This physics-based, data-driven approach allows us to infer internal technical parameters of industrial plants’ production stages using only smart meter data at 15-minute or hourly resolution—something previously thought impossible.
Research Journey and Publication Challenge
This work represents a significant paradigm shift in industrial load modeling. Due to its novelty and counter-intuitive findings, our paper underwent an extensive review process spanning nearly two years, as we worked to convince reviewers of the technique’s validity and implications. The eventual publication validates our approach and opens new possibilities for industrial load integration in power systems.
Resources and Implementation
We have open-sourced our methodology to enable other researchers and practitioners to apply these techniques:
- GitHub Repository: https://github.com/Rick10119/Production-Scheduling-Identification
- Explanation Video: Link to Bilibili video explaining the method
Impact
This breakthrough enables:
- Virtual power plants to accurately model industrial loads without requiring sensitive internal data
- Power system operators to better assess demand response potential from industrial users
- More effective integration of industrial flexibility into grid operations
- Preservation of industrial users’ privacy while enabling their participation in energy markets
By solving this long-standing data barrier, our work helps bridge the gap between theoretical industrial load flexibility and practical implementation at scale.
Citation Format: R. Lyu, H. Guo, Q. Tang, Q. Chen and C. Kang, “Production Scheduling Identification: An Inverse Optimization Approach for Industrial Load Modeling Using Smart Meter Data,” in IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, doi: 10.1109/TSG.2024.3507046.