Co-Optimization of Bidding and Control for Heterogeneous Resources in Power Markets
Published in IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid/Applied Energy, 2023
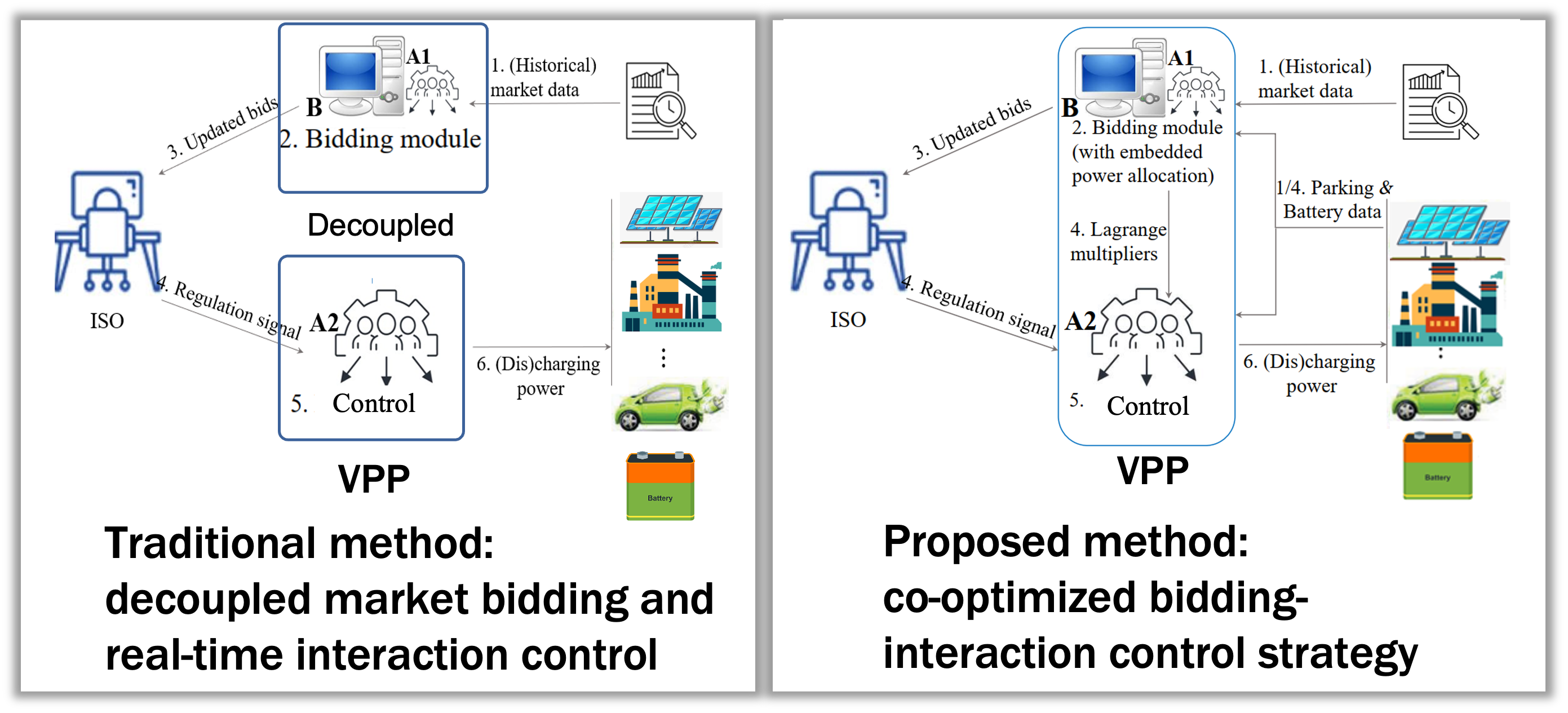
From Models to Market Participation
Having developed accurate models, parameter identification methods, and dimension reduction techniques, the final challenge is implementing effective interactions between industrial users and power grids. This research area focuses on the economics of these interactions and how to minimize costs while maximizing benefits for all participants.
The Coordination Challenge
When aggregating heterogeneous resources into a virtual power plant (VPP) to participate in power markets, several critical challenges emerge:
Resource Heterogeneity: Different types of resources—industrial loads, electric vehicles, thermostatically controlled loads, distributed energy storage, and distributed energy resources—have distinct characteristics and constraints described by different models
Real-Time Decision Requirements: Participation in services like regulation requires responding to signals sent at 2-4 second intervals, necessitating extremely fast decision-making
Scale and Complexity: Controlling thousands of resources while considering uncertainty and different models creates significant computational challenges
Temporal Coupling: Control decisions affect future bidding capabilities, while bidding strategies influence control decisions, creating complex temporal dependencies
Co-Optimization Framework
Our first major contribution in this area is developing a framework to co-optimize bidding and control of virtual power plants in power markets (published in IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2023). Previous approaches used simplified strategies without co-optimization, resulting in reduced profits.
This co-optimization approach balances:
- Immediate costs induced by current control decisions
- Future profits affected by bidding strategies
- The interdependence between bidding and control decisions
TSG-2023 Github (code and slides) Video
Real-Time Implementation Strategy
Building on the co-optimization framework, we implemented this approach in a case where industrial resources are coordinated to provide services to the power grid (published in Applied Energy, 2024). Our implementation includes:
- Standardized Resource Models: Creating consistent models for different resource types
- Error Compensation: Accounting for errors introduced during parameter identification and dimension reduction
- Computational Efficiency: Developing strategies that can execute within tight time constraints
Arithmetic-Only Control Strategy
Perhaps most remarkably, we developed a method that uses only basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) to calculate real-time control actions. This eliminates the need for deploying optimization solvers online, which is critical for practical applications where:
- Computation must be completed in milliseconds
- Resources may have limited computational capabilities
- Implementation must be robust and simple to deploy at scale
Impact on Market Integration
This research completes the pipeline from modeling to market participation, enabling industrial users and other flexible resources to be efficiently integrated into power markets. The economic benefits are substantial, with our co-optimization approach demonstrating significant profit improvements over conventional methods.
By solving the economic challenges of heterogeneous resource coordination, we make it feasible for industrial users to provide valuable services to the grid while maintaining their primary production objectives—creating a win-win situation for both industry and the power system.